Introduction
There are many industrial applications that cause soil contaminations such as petroleum drilling, petroleum refineries, power generation, mining, military, manufacturing industries etc. where the wastes generated from these industries, Soil Contaminated, may include hydrocarbons, heavy metals, hazardous & toxic chemicals in different concentration’s, these contaminants will consequently reduce the soil fertility and biological activity when deposited in it, as they affect the soil layer strength and might even affect the ground water.

Soil Remediation Process
SMIW Co. Soil Remediation process entails recovering the oil/ hydrocarbon from the oil/ hydrocarbon contaminated soil to the maximum extent possible, or stabilization of the contaminated soil by high levels of heavy metals or other contaminants such as acid/ alkaline materials. All the treatment processes shall be within the acceptable environmental regulations as possible for zero hazardous waste disposal.
Depending on the characteristics of the contaminated soil and its analyses report of the contaminated soil SMIW Co. identifies the proper methodology for the remediation process which can be for example stabilization, thermal desorption, incineration etc.
SMIW Co. have an adequate experience in contaminated soil remediation for more than two decades and had served many projects in Saudi Arabia and GCC region,

Thermal Desorption is an American technology invented in 1985 that physically separates volatile and semi-volatile hydrocarbon pollutants from contaminated soil, sediment, and oily sludge by indirect heating to high temperatures (usually between 170 to 450 °C) and under vacuum pressure so that the hydrocarbon compounds are recovered from the stream of gases resulting from the heating process through a specialized condensing system and returned to use as for purpose.
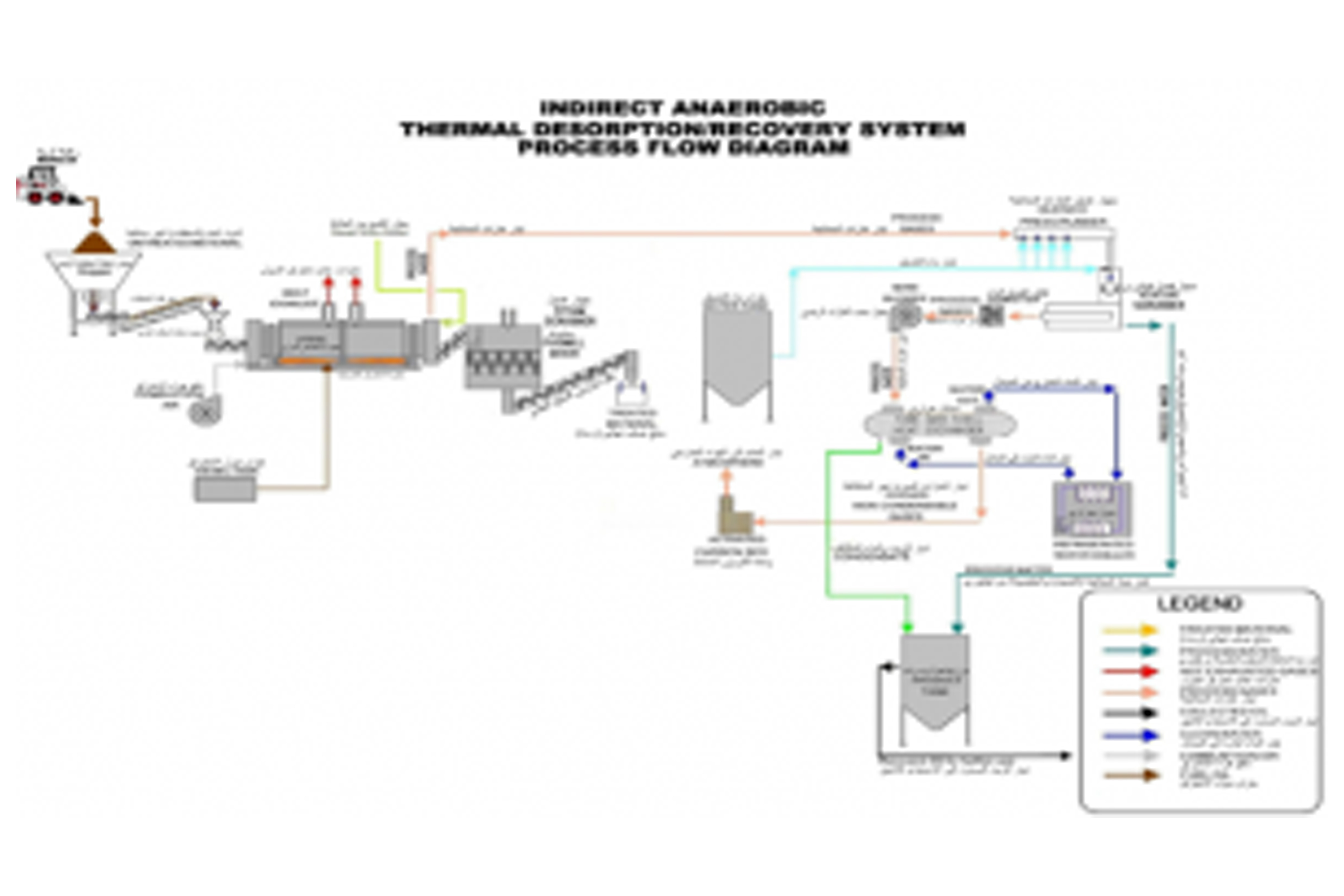
Process Criteria
The remaining treated soil or will be further treated by Thermal Desorption Unit to meet the TPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) content less than 1%. then either to return the treated materials or to discard and replace it, all of that is according to as per the environmental rules and regulations.
Remediation Process
- Recover 99.9% of the hydrocarbons in the waste
- Mobile unit with the possibility of rapid intervention in case of emergency
- Preserving natural resources by recovering oil and water for reuse
- Significantly reduce disposal and incineration costs
- Detoxify solids and convert them into inert materials for safe disposal
- Valuable resource recovery and recycling
- Operational flexibility and production capacity
Soil Remediation by Stabilization
SMIW Co. is used to receive and remediate contaminated soil with heavy metals, acids and alkaline materials by Solidification/ or and Stabilization to reduce the solubility or mobility of the contaminants to the surrounding environmental.
The process entails introducing binding agents such as cement and lime material to the contaminated soil, this is for restricting the migration of contaminants by minimizing their available surface area, and converting the hazardous constituent into a non-hazardous form, this can be achieved by actual chemical or/ and physical interaction, then the stabilized formation will be disposed into Class I Landfilling. Below figure shows the process flow diagram of the unit:
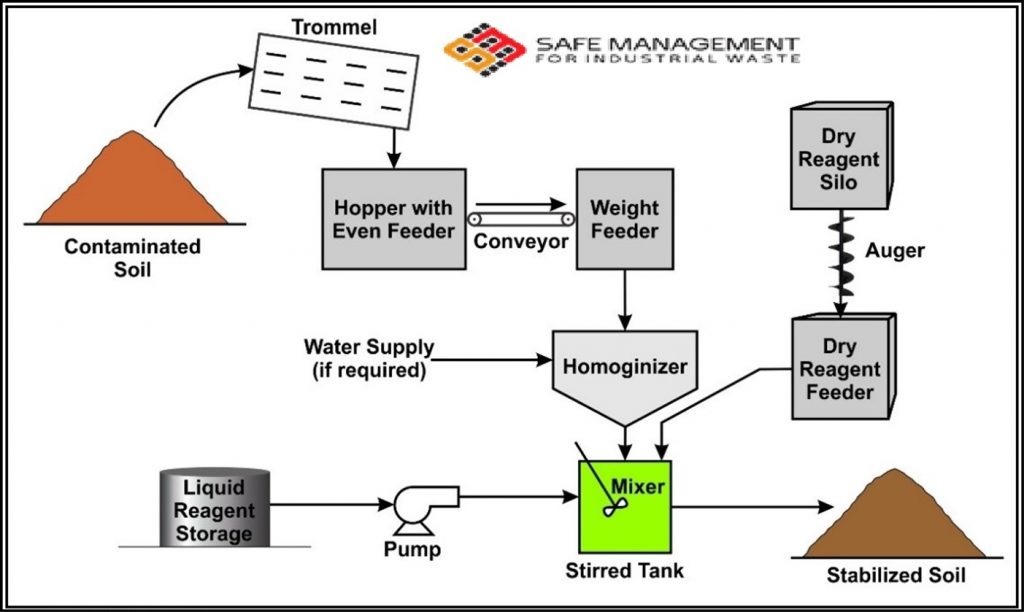
Stabilization Process
- Enabling the treatment of complicated mixtures of different wastes streams.
- Effective in treating materials contaminated with some types of organic & volatile chemicals.
- Cost effective method as the binding agents are relatively inexpensive.
- The treatment end point can be achieved relatively quickly.
- Possibility of improving the structural properties of soil, waste, and sludge (such as strength) which enable of the reuse.
- The process can be done both in situ and ex situ treatment.
- Simple, readily available equipment and materials are used.
- If done On-site, It will conserves landfill and transportation costs.
- Does not need high levels of skill.
- More cost effective than excavation and off-site disposal.

